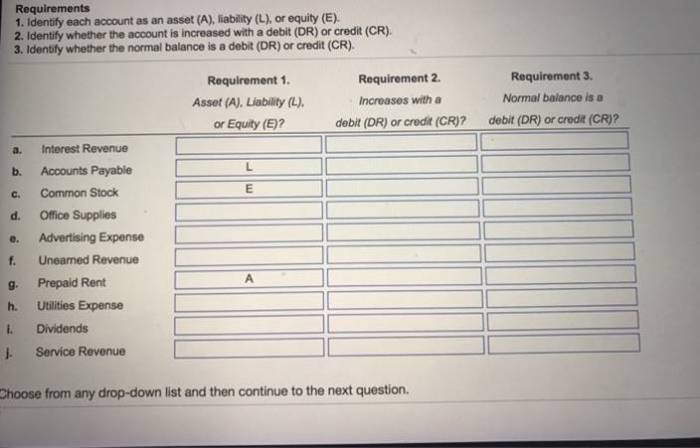
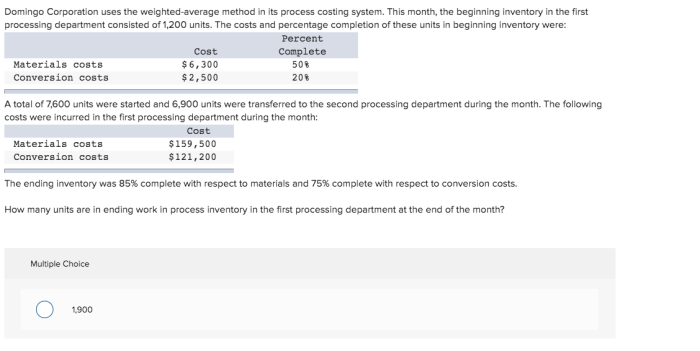
Identify each account as asset liability or equity – In the realm of accounting, the accurate classification of accounts as assets, liabilities, or equity is paramount for maintaining financial integrity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of account identification, providing a solid foundation for understanding the balance sheet equation and the impact of transactions on financial statements.
By mastering the principles Artikeld in this guide, individuals can effectively classify accounts, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting.
Identify Account Types
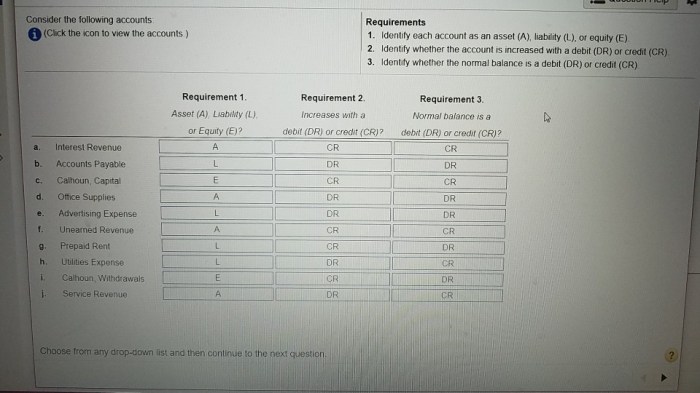
Understanding the different types of accounts is crucial for effective financial reporting. Accounts are classified into three main categories: assets, liabilities, and equity.
Assets represent resources owned or controlled by a company that have economic value. They include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and property.
Liabilities are obligations owed by a company to other parties. They include accounts payable, notes payable, and bonds payable.
Equity represents the ownership interest in a company. It includes common stock, retained earnings, and other equity accounts.
Balance Sheet Equation, Identify each account as asset liability or equity
The balance sheet equation is a fundamental accounting concept that states that the total assets of a company must equal the sum of its liabilities and equity.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This equation ensures that the financial statements are balanced and that the company’s financial position is accurately represented.
Impact of Transactions
Transactions affect the balance sheet equation by changing the balances of specific accounts.
- When a company purchases inventory, the inventory account increases (an asset), while the cash account decreases (an asset).
- When a company issues a bond, the cash account increases (an asset), while the bonds payable account increases (a liability).
- When a company earns revenue, the revenue account increases (an equity), while the cash account increases (an asset).
HTML Table Structure
An HTML table can be used to organize and display account information in a structured manner.
| Account Name | Type | Balance |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | Asset | $10,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | Asset | $5,000 |
| Inventory | Asset | $2,000 |
| Accounts Payable | Liability | $3,000 |
| Notes Payable | Liability | $2,000 |
| Common Stock | Equity | $10,000 |
Account Classification Examples
- Cash – Asset
- Accounts Receivable – Asset
- Inventory – Asset
- Property, Plant, and Equipment – Asset
- Accounts Payable – Liability
- Notes Payable – Liability
- Bonds Payable – Liability
- Common Stock – Equity
- Retained Earnings – Equity
- Other Comprehensive Income – Equity
Methods for Classifying Accounts
There are different methods used to classify accounts, including:
- Liquidity:This method classifies accounts based on their convertibility into cash.
- Permanence:This method classifies accounts based on their expected duration.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific needs of the company.
Procedures for Identifying Account Types
- Determine the nature of the transaction.
- Identify the accounts affected by the transaction.
- Determine whether the account is an asset, liability, or equity account.
- Classify the account accordingly.
Common Errors in Account Classification
- Misclassifying assets as liabilities or vice versa.
- Misclassifying expenses as assets.
- Misclassifying revenues as liabilities.
- Failing to consider the nature of the transaction.
These errors can lead to inaccurate financial statements and incorrect financial decisions.
Question & Answer Hub: Identify Each Account As Asset Liability Or Equity
What is the difference between an asset and a liability?
An asset is an economic resource that is owned by a company and has future economic value, while a liability is an obligation that a company owes to another party.
How does the balance sheet equation work?
The balance sheet equation states that assets are equal to liabilities plus equity. This equation must always balance in order for the financial statements to be accurate.
What are some common examples of assets?
Common examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and equipment.
What are some common examples of liabilities?
Common examples of liabilities include accounts payable, notes payable, and bonds payable.
What are some common examples of equity?
Common examples of equity include common stock, preferred stock, and retained earnings.